
The ecommerce industry is leading a renaissance in the ad industry, and Google Ads is serving as one of the primary marketing channels at the forefront of the unprecedented boom.
With Google Ads accounting for almost 20% of all ecommerce revenues, it’s easy to see why it’s one of the most-utilized ad networks for this business type.
We understand the apprehension, though — Google Ads can be daunting for most ecommerce business owners with all its bells and whistles.
That’s why we’ve come up with this handy resource showing ecommerce businesses how to get set up with Google Ads for ecommerce to drive growth, traffic, and conversions. We’ll also share tips and tricks on how to leverage the platform effectively by following our best practices.
Understanding Your Target Demographic and Setting Goals
The first step ecommerce businesses need to do is to determine the target audience for their ecommerce store. Creating highly personalized Google ecommerce campaigns that target specific audiences based on their localization preferences will help you tailor your marketing materials and products to maximize ROI on ad spend.
This requires the creation of buyer personas.
Buyer personas refer to fictional, idealized representations of your target customers based on data and market research. By identifying audiences that resemble your buyer personas the most, you can ensure that your Google ads are displayed to individuals that are likely to be interested in your ecommerce products and services.
Google Ads will allow you to refine the granular details and define groups of potential shoppers in the locations you select sharing the same browsing habits, demographics, and interests. You can build buyer personas in this section.
It also allows you to create custom campaigns depending on your campaign goals, which may include conversions, lead generation, web traffic, product/brand consideration, and brand awareness/reach, among others.
Here are some of the most common ecommerce Google Ads campaign goals you can set:
- Sales. Sales campaigns are designed to increase in-store, in-app, or mobile sales using a variety of search ads, display ads, shopping ads, and video ads campaign types.
- Leads. Leads campaigns are designed to persuade potential customers to take a specific action to help generate leads and conversions.
- Web Traffic. Want to drive targeted, organic traffic to your ecommerce store? Choose this goal.
- Product and Brand Consideration. This goal is what you’ll want to choose if you want to encourage potential customers to explore your product and service portfolio.
- Brand Awareness and Reach. This campaign goal, meanwhile, helps boost your exposure and reach wider audiences using display ads and video campaigns.
Keyword Research and Selection
Next up, it’s time to conduct keyword research and selection.
There are several factors that go into this process besides just finding the right keywords for your pay-per-click campaigns – and it’s not always about picking the keywords that get the most searches.
Instead, the goal is to strike a balance between search volume and what gives you the most bang for your buck. This is where long-tail keyword research comes in.
While shorter keywords may get higher search volumes, long-tail keywords will help you get more conversions from qualified leads with significantly less competition at a lower cost.
Here are some best practices when it comes to keyword research and selection for keyword research and selection:
- Conducting competitor keyword research. One of the tried and tested ways to find keywords with high potential is to see what your competitors are already using for their Google Ads for ecommerce. Try conducting searches for your leading competitors’ brand names and products, and scroll down to see the text search ads that are shown on the SERPs. Many of them will be bidding on those keywords.
- Use keyword planning tools. Subsequently, you can also use premium keyword research tools to see what other keywords your competitors are bidding on. Keyword research and planning tools like Google Keyword Planner or SEMrush can help you find keywords with excellent search volumes, lower competition, and more value for money. Incorporate these keywords into your content, URLs, meta tags, and headings for the best results.
- Use ad groups for better organization. Another good practice is to group keywords by themes into ad groups. For instance, use only the keywords that are relevant to the landing pages you wish to direct traffic to. If your ads are irrelevant to your landing pages and search queries, you’ll struggle to convert. Use targeted keywords from your Ad Groups to craft better ecommerce Google ads.
Creating Compelling Ad Copy That Converts
Engaging new customers and getting conversions requires compelling ad copy. The following factors will always help you craft copy that converts, regardless of platform:
- Clear, attention-grabbing headlines. First impressions last, and your headline will determine if your ad will draw. Your headlines should be concise, clear, and directly communicate your product’s unique selling proposition. A good headline will hook in leads and want them to learn more.
- Use persuasive verbiage. Every word counts. Therefore, your ad copy should directly convey your message and selling proposition in the most concise and persuasive manner possible. Focus on how your product directly addresses your audience’s pain points.
- Use a strong call-to-action (CTA). A call-to-action (CTA) is a must-have element that helps tell your audiences the next action they should take. CTAs should likewise be clear and concise to elicit the desired effect and immediate response. Some examples of CTAs that create a sense of urgency include “Buy now,” “Register Now,” and “Sign Up Today.”
But the work is far from over. In order to find your winner you will need to A/B test…a lot. You could do it on your own, or you could try Tailwind Ghostwriter that will give you days’ (weeks’?!) worth of copy ideas in a matter of seconds.
Setting Budgets and Bids
Now, it’s time to determine your budgets and bids. Obviously, your Google Ads budget will depend on your niche within the ecommerce industry, the size of your company, and how you manage your Google Ads account (e.g. how much you are willing to spend). There is no one-size-fits-all answer here.
That said, how do you determine your budget size? First, you can use data from your existing marketing plan to help inform how you should set up your Google Ads account structure and budget. You can set a total campaign or daily budget accordingly depending on your needs. Google Ads runs on a pay-per-click (PPC) basis, meaning you’ll only be charged when someone actually clicks on your ad.
We highly recommend starting with a small “test” budget if you’re handling your ecommerce Google ads yourself. Then, once you’ve gotten a better feel for the platform and your Google ad campaigns, you can progressively increase your ad spend as necessary.
You can reduce your learning curve in budgeting for Google Ads by:
- Leveraging competitor keyword research to see how your closest competitors are running their campaigns;
- Establishing the most relevant key performance indicators for your ecommerce business;
- Basing your ad spend on your business goals and existing resources.
Bid Strategy for Google Ads
There are various bidding strategies for Google Ads, and the best one for your campaign depends on your goals. The most prevalent Google Ads bid strategies for ecommerce are manual bidding, automatic bidding, and target cost-per-acquisition (CPA) bidding.
- Manual bidding. Manual bidding is the most commonly used bidding strategy because of its simplicity. Just set a maximum cost-per-click (CPC) bid for every keyword, and you will only be charged when someone clicks on your ad. Manual bidding gives you greater control over your budget and bids, making it a great choice to begin with. The only downside is that manual bidding can be a bit tedious because you need to set up your bids for every target keyword you wish to use.
- Automatic bidding. Automatic bidding has Google set your bids based on your campaign goals. While it may be helpful and more efficient if you’re unsure about manually setting up your bids, you lose a degree of budgetary control. However, it can lead to unpredictable results. Worse, it could exhaust your budget.
- Target CPA bidding. Target CPA bidding is a bid strategy based on how much it costs you to acquire customers. This is a good choice if you wish to optimize conversions, but can be a bit more complex to set up and do right.
Not sure where to start? Try manual bidding first and see how well your ad campaigns perform. Then, try out more complex strategies to see what works best for you depending on your goals and budgets.
Using Google Ads Asset (former Extensions)
Google Ad extensions are those snippets of valuable information about your ecommerce site, products, or services that appear in your ad descriptions. These may include seller rating extensions, callout extensions, price extensions, sitelink extensions, location extensions, structured snippets, and promotion extensions.
Google Ad extensions help you get more valuable screen real estate in the SERPs, helping boost your chances of getting clicks. Google Ad extensions typically appear if you rank around the top 3 of the SERPs. They may show up if you rank lower than that, but they will be less visible as you go down the SERP rankings.
Sitelinks, as shown in the example below, have been around for quite a while. Most Google Ads accounts have at least a few of them active.
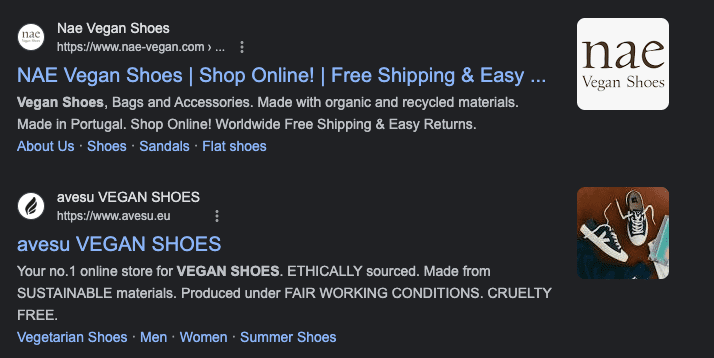
Ecommerce brands can leverage Google Ads extensions such as price extensions, structured snippets, and promotion extensions — all of which can help distinguish their products and services from the rest of their competition.
A good practice for ecommerce brands is to set up several Google Ad extensions so its algorithm can work its magic and display the ones that work best.
Optimizing Ad Campaigns, Tracking and Measuring Performance
Finally, optimizing Google Ads campaigns can help drive conversions and sales without exceeding your ad spend. But in order to optimize your Google Ads campaigns, you need to track and measure closely how your campaigns are performing.
Here are some top optimization tips for your ecommerce Google Ads campaigns:
- Install and use Google Analytics. Google Analytics is an essential tool to help you track engagement, traffic, and conversions. Using real-time and historical data, you can pinpoint trends, track demographics, and identify areas that need improvement.
- Use Google Ads conversion tracking to measure the success of your ad campaigns. Conversion tracking allows advertisers to determine the return on investment (ROI) of their advertising efforts. By analyzing conversion data, you can identify which campaigns generate the most revenue and adjust your budget accordingly. Adjust keyword bids, ad copy, and targeting settings to improve ROI and conversion rates.
- Track the appropriate metrics. To tangibly measure how well your Google Ads campaigns are hitting, you need to monitor the right metrics. For PPC campaigns, click-through rate (CTR), conversion rate, cost-per-click (CPC), and return on ad spend (ROAS) are the metrics that will give you insights on how your campaigns are performing — as well as areas for improvements.
- Conduct A/B testing. Based on performance data, regularly optimize your ad campaigns by running A/B tests on ad elements (you can find it under the Experiments section). Visual assets, ad copy, targeting options, and landing pages can all be tweaked to determine which combinations work best in terms of campaign effectiveness.
Conclusion: Best Google Ads Types for Ecommerce Brands
Google supports a wide array of Google Ads and Campaign types. However, not all of them are applicable to ecommerce. In closing, here are the best Google Ads and Campaign types for ecommerce:
- Google Shopping Ads. Product Listing Ads allow you to generate traffic and highlight your products and services. They show up as image-based ads with price information, reviews, and other essential pieces of information.
- Google Search Ads. Google Search ads appear on the SERPs of the Google Search Network when a user types in a related keyword. To create search ads, you need to do keyword research, produce ad copy, and set a budget as discussed earlier. You can also determine where your ad will appear and how frequently it will appear.
- Dynamic Search Ads (DSAs). Dynamic Search Ads are a type of ad that is automatically generated based on your site contents. How do you create DSAs? First, you need to set up an ad campaign and create an ad group specifying which web pages you wish to target. Google takes care of the rest, creating ads based on said pages.
- YouTube Ads. YouTube video ads are another effective way to reach ecommerce audiences, given the number of users on the platform searching for videos about the products and services they wish to buy.
- Google Performance Max Campaigns. Google Performance Max ad campaigns allow you to pay a fixed price for every conversion produced by way of your ads, allowing you to maximize your ecommerce advertising budget.
- Google Smart Shopping Campaigns. Another ad campaign type that works well for ecommerce is a Google Smart Shopping campaign. These campaigns harness AI to automatically allocate and optimize your budget across Google verticals, such as Google Search, Google Display, Gmail, and YouTube, among others.
- Google Display Network. Google Display Network is a network of sites that collaborate with Google to display ads. Simply choose an image or video for your ad, create your copy, and set a budget. You can also determine how often you want your ads to be shown and where they appear.
- Google Retargeting Ads (Google Remarketing Ads). Finally, Google Remarketing/Retargeting Ads are another effective option for ecommerce because they target individuals who have already visited or engaged with your ecommerce site. Google uses browser cookies to track online activity and identify the people most likely to convert.







